Mastering Your Migration to Tableau Cloud: Challenges, Solutions, and Success
Smoothly Transition from Tableau Server to Tableau Cloud with Confidence
Why Tableau Cloud?
As organizations embrace the power of the cloud, Tableau Cloud (formerly Tableau Online) has become a leading solution for analytics and collaboration. With Tableau Cloud, businesses can eliminate infrastructure management, gain global accessibility, and always stay updated with the latest Tableau features. However, migrating from Tableau Server On-Premise to Tableau Cloud isn’t without its challenges.
This newsletter provides a comprehensive guide to migrating successfully, highlighting potential obstacles, tools to streamline the process, and actionable steps to ensure long-term success.
Why Choose Tableau Cloud?
Tableau Cloud offers an all-in-one analytics platform that simplifies data sharing and collaboration across the organization.
Key Benefits:
No Infrastructure Management: Tableau handles upgrades, backups, and scaling.
Global Access: Teams can access dashboards securely from anywhere.
Automatic Updates: Always use the latest features without manual upgrades.
Enhanced Collaboration: Simplified sharing and interaction across geographies.
Scalability: Tableau Cloud grows with your needs, avoiding server limitations.
Challenges in Migrating to Tableau Cloud
Migrating to Tableau Cloud is rewarding but comes with unique challenges that require careful planning.
1. PostgreSQL Repository is No Longer Available
Tableau Server's PostgreSQL repository provided detailed metadata and audit capabilities. Tableau Cloud doesn’t offer direct access to this database.
Impact: Difficulty in generating historical usage reports and tracking detailed metadata.
2. Metadata Refresh Limitations
Tableau Cloud does not currently support real-time metadata refresh for all content. Changes in data sources, dashboards, or permissions may not reflect instantly in metadata-related tools.
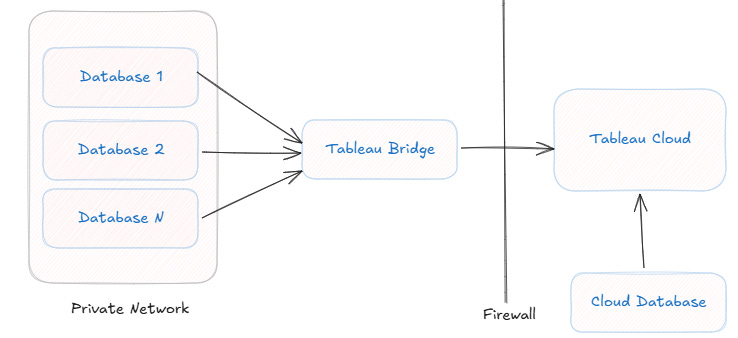
3. Connectivity to Local Data Sources
On-premise data sources require Tableau Bridge to connect securely to Tableau Cloud. This introduces complexity in managing and monitoring connections.
4. Migration of Custom Views and Subscriptions
Custom views and subscriptions are not automatically migrated. They must be recreated manually or via API automation.
5. Permission Inconsistencies
Permissions from Tableau Server may not directly translate to Tableau Cloud, leading to potential mismatches.
6. Performance Adjustments
Dashboards optimized for Tableau Server may require redesign to ensure optimal performance in Tableau Cloud due to differences in infrastructure and query execution.
Tools to Simplify Migration
Tableau Migration Tool:
Automates the transfer of projects, workbooks, and data sources but requires manual work for custom views and subscriptions.Tableau Bridge:
Ensures secure, continuous connectivity between Tableau Cloud and on-premise data sources.API REST:
Enables programmatic recreation of users, permissions, subscriptions, and even metadata extraction.Performance Recorder:
Identifies bottlenecks and optimizes dashboards for better performance in Tableau Cloud.
12 Steps to a Successful Migration
Step 1: Conduct an Audit
Inventory dashboards, workbooks, extracts, users, groups, permissions, and schedules.
Identify and prioritize critical dashboards and high-frequency extracts.
Step 2: Plan the Migration
Define priorities and migration phases (e.g., live connections first, followed by extract-based dashboards).
Communicate the migration roadmap with stakeholders.
Step 3: Prepare Tableau Cloud
Set up projects, groups, and permissions in Tableau Cloud.
Install and configure Tableau Bridge for local data sources.
Step 4: Migrate Users
Export user details from Tableau Server.
Upload users and groups to Tableau Cloud using a CSV file or API.
Verify roles and permissions.
Step 5: Optimize Workbooks
Review dashboard calculations, filters, and data source connections.
Simplify and consolidate complex queries where possible.
Step 6: Migrate Live Connection Workbooks
Publish dashboards with live connections to Tableau Cloud.
Validate connectivity and query results using Tableau Bridge if needed.
Step 7: Migrate Extracts
Transfer extracts using Tableau Migration Tool or Tableau Desktop.
Reconfigure and validate scheduled refreshes.
Step 8: Handle Custom Views
Document existing custom views using Tableau Server PostgreSQL.
Recreate critical views manually or with API automation.
Step 9: Recreate Subscriptions
Document subscriptions, including schedules and recipients.
Recreate subscriptions in Tableau Cloud manually or programmatically.
Step 10: Validate Migration
Compare data and performance between Tableau Server and Tableau Cloud.
Test permissions, refresh schedules, and user access comprehensively.
Step 11: Train and Support Users
Conduct training sessions highlighting Tableau Cloud’s new features.
Provide documentation for common tasks like subscriptions and managing permissions.
Step 12: Optimize Post-Migration
Consolidate redundant extracts and retire unused dashboards.
Monitor adoption using Tableau Cloud’s admin views and usage metrics.
Address metadata lag by proactively auditing changes in data sources and permissions.
Post-Migration Activities
Once the migration is complete, focus on fine-tuning Tableau Cloud to maximize its benefits.
Validate and Monitor
Ensure all dashboards, permissions, and subscriptions function as intended.
Regularly monitor performance using admin views and address user feedback.
Optimize Dashboards
Simplify filters, calculations, and data sources to improve query execution.
Identify and fix slow-loading dashboards with Performance Recorder.
Refine Permissions
Regularly audit group-based permissions to ensure they align with business needs.
Provide Continuous Support
Offer ongoing training for users adapting to Tableau Cloud.
Maintain a clear support structure for addressing issues.
Conclusion: Overcoming Challenges to Unlock the Benefits of Tableau Cloud
Migrating to Tableau Cloud is a significant milestone that unlocks enhanced collaboration, reduced IT overhead, and improved scalability. While challenges like the absence of PostgreSQL and metadata refresh limitations require careful handling, following a structured migration process ensures success.
With the right tools, planning, and post-migration activities, your organization can fully leverage Tableau Cloud’s capabilities to drive data-driven decisions.